National Authority for Remote Sensing and Space Sciences
- Owner NARSS
- Area 4483 m2
- Cost 25 000 000 $
- Date Under Construction
- Description Research Building
- Service Planning, Design & Landscape for all stages, Detailed design, Construction management, Site supervision and project management for first stage.
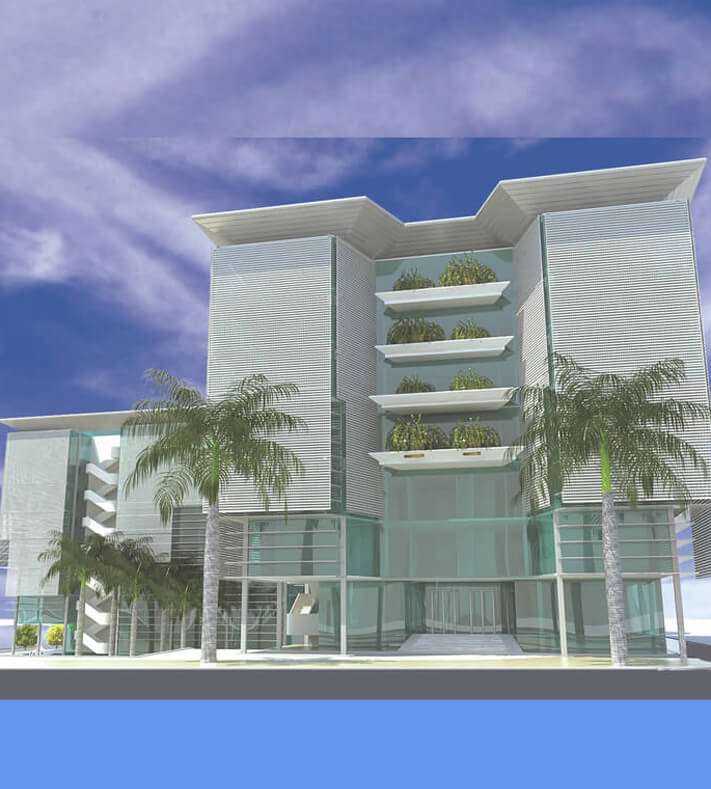
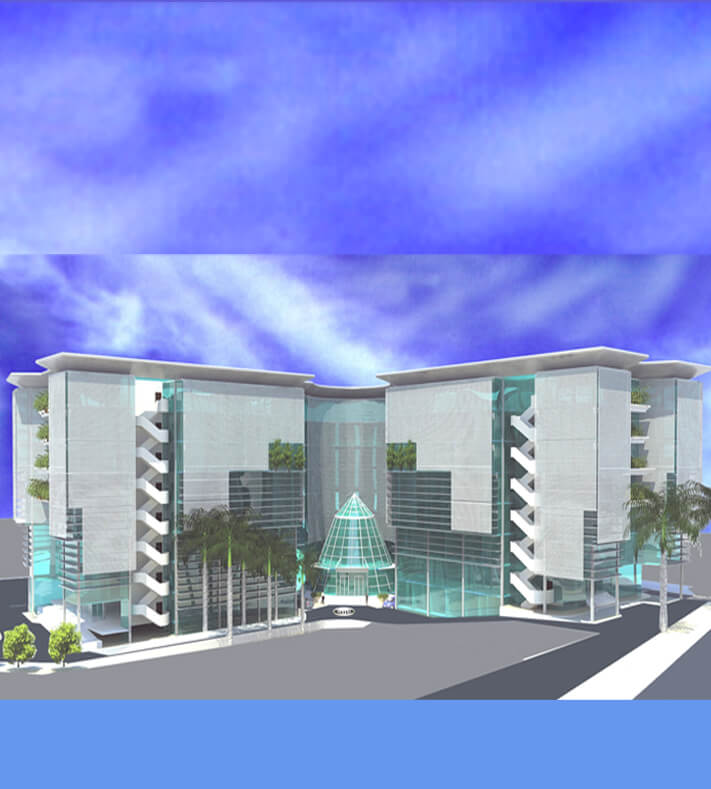
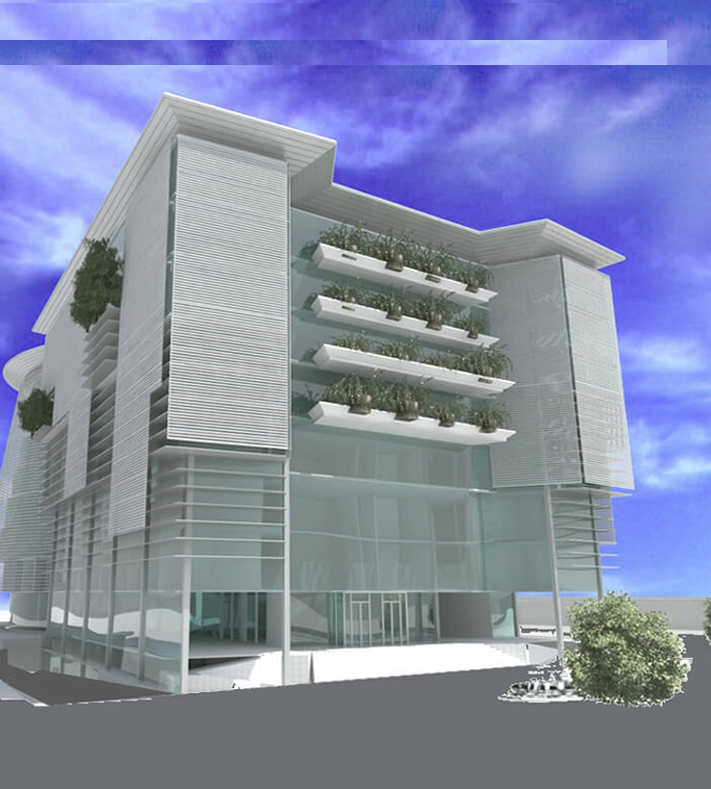
Project Description
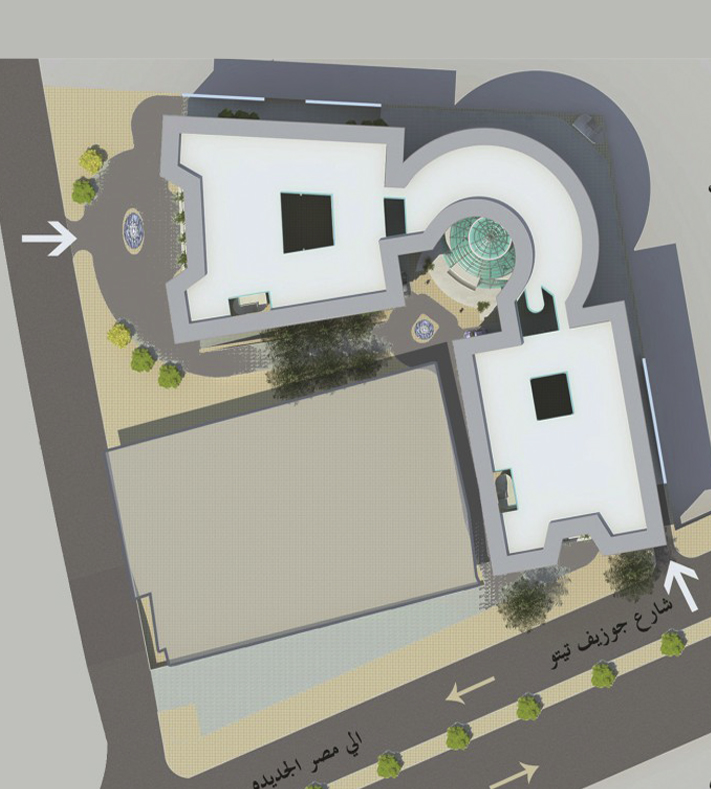
The project was studied within the framework of the surrounding natural and urban environment and to provide the greatest degree of integration within the building, as well as to achieve the modern functional requirements of the National Authority for Remote Sensing and Space Sciences. Therefore, the building is designed as a sustainable building that achieves the employment of the most efficient contemporary technologies and the mental image that expresses scientific progress and the space age. The building also uses advanced environmental technologies. The building was designed to consist of three main blocks: (A), (B) and (C), one of them is a block overlooking the Joseph Tito axis, which is one of the largest and most important developmental traffic axes in Nozha area to free the building block from the borders of the land with the neighbor to achieve Architectural independence. The entrance to the building from this axis resembles the containment of the block between two arms extending outward to confirm the entrance. The block extended to take the shape of the letter L in English to repeat the formation of the entrance from the Scientific Research Street. Blocks (A) and (C) were allocated to resemble the growth of the mass, and in the middle of them is block (B) which is part of the building in the shape of a crescent, as if it were a hinge, and it was allocated to the higher administration, laboratories and the information center, and this provided an internal large space for the main entrance. An open courtyard was provided for each block in order to achieve natural lighting and a suitable quiet environment for research and studying. The building's outer shell has been treated by providing sun breakers that block the unwanted sun in the hot summer and allow the sun to enter during the cold winter periods. This is done by making a disparity within the distances between the breakers and making them gradual to maximize the shadows during the hot periods.
Our Gallery